Gum Recession in Bel Air
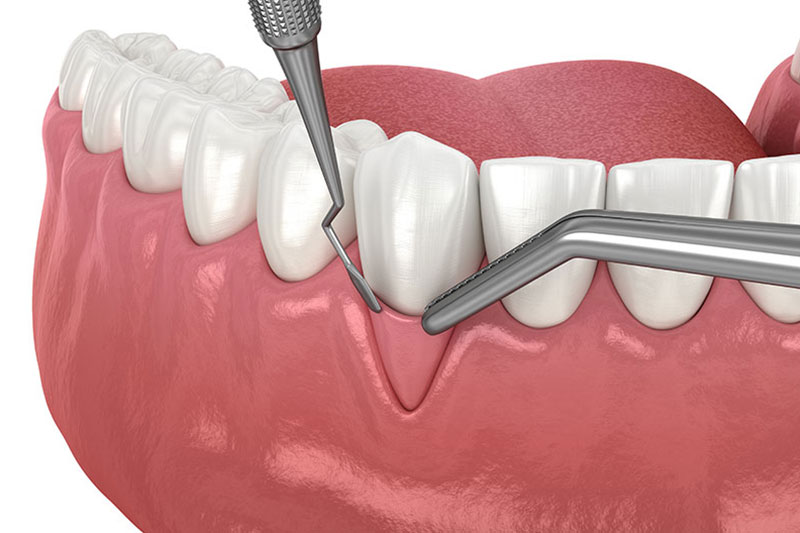
Gingival recession is a problem which effects millions of Americans. It may be caused by toothbrush abrasion, periodontal disease or simply as a product of aging. When gingival recession occurs the teeth appear longer, the root surface is exposed and generalized sensitivity of the teeth occurs. These problems can all be addressed by the use of gingival grafting. This is a procedure where we can literally move the gum to a position that covers more of the tooth structure. This can also be accomplished by using graft tissue – either an autograft from the patient’s palate or a synthetic graft to cover the exposed tooth surfaces. Any type of this procedure will alleviate the sensitivity and will allow for an outstanding aesthetic result.
Soft Tissue Corrective Grafts
In addition to the development of pockets and bone loss, periodontal disease can cause the gums to recede, thereby exposing the roots of the teeth. When the root of a tooth loses its overlying soft tissue, it becomes more vulnerable to decay, sensitivity, and additional bone loss. Gum recession also takes a toll on smile aesthetics. Having front teeth affected by this problem can make a broad smile less aesthetically appealing as uncovered root structure is displayed. While gum recession may be one of the consequences of gum disease, aggressive tooth brushing, and other habits can also wear away gum tissue.
By performing a gum graft procedure, which is also known as a "gingival graft or soft tissue graft," we can replace the soft tissue over the exposed area of the tooth to address the problems created by receding gums. A gum graft may be performed on a single tooth or multiple ones. And, based upon the needs of the case, our periodontist will determine which type of gum graft to employ.
The three types of gum grafts include the following:
- Free gingival graft-This graft utilizes a small piece of tissue that is taken from the palate. It is often indicated when extra thick tissue is needed to prevent further recession.
- Connective tissue graft- This frequently used graft is harvested from a sub-layer of connective tissue located under the uppermost tissue layer on the roof of the mouth.
- Pedicle graft-This type of graft is created from a flap of tissue that is adjacent to the area of the gum recession.
Following a gum graft procedure, our office will provide detailed post-operative care instructions as well as set up appointments to make sure the surgical site is healing properly and to check that the graft is successful.
Gingivectomy - The Removal of Excess Gum Tissue
Excessive gum tissue and overgrowth can develop for a number of reasons. It may be due to inflammation, systemic disease, a genetic condition, or as a side effect of certain medications. The type of treatment depends on the underlying cause. While gingivitis, which is the first stage of gum disease, may respond to improved oral hygiene and non-surgical periodontal treatment, a gingivectomy may be the best way to address overgrown gum tissue due to medication or disease.
During a gingivectomy, our periodontist removes a precise amount of tissue around the affected teeth and then sculpts the gumline to improve smile aesthetics and support good oral health. Typically performed under local anesthesia, a gingivectomy can involve either a single tooth or multiple teeth, as indicated. Following the procedure, patients are provided with detailed post-operative instructions.

